
What is the Difference Between Casein and Whey Protein - Recommended H1 tag For starters let us look at the similarities between them both. Both Casein and Whey are made from milk. They are both dairy proteins. Both are high quality complete proteins highly sought after for their muscle recovery support.
Now that the similarities are out of the way, let us dive into how Casein and Whey proteins are unique in their own ways.
Whey Protein & Casein Protein: The differences
- How Much Casein/Whey is there in the milk?
With 80% of protein in milk being casein, it is considered as the major milk protein. In a typical 240ml glass of milk you get ~8 grams of protein and 80% of which is Casein. Whey on the other hand is considered as the minor milk protein as only 20% of milk proteins are whey which in a cup of milk comes up to 1.6 grams of whey.

- Casein Trivia: Milk gets its milky white colour due to casein. Milk is white because there are ~1,000 trillion Casein molecules per millilitre of milk.
- Whey Trivia: You need ~3.5 litres of milk to derive 24 grams of whey protein.
- Sources of Casein/Whey
- Casein: Milk, Paneer, Cheese, Yogurt, Casein Protein Powders.
- Whey: Liquid whey, and whey protein-based supplements.
- Speed of Digestion
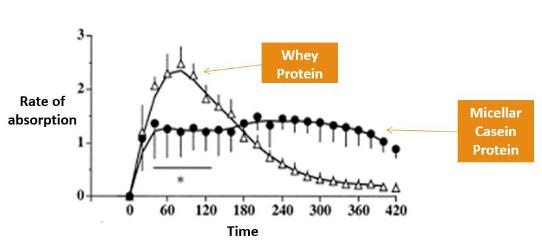
Whey protein is considered as a fast digesting and absorbing protein as compared to casein. Amino acids from whey protein will peak in the bloodstream in about an hour after consumption, whereas amino acids from casein are released slowly over many hours. - Amino Acid Composition of Casein?
Both Casein & Whey are complete proteins, meaning it contains enough quantities of all the 9 essential amino acids.
Typically, in 24 grams of casein you will get about 9 grams of Essential Amino Acids (EAAs) including about 5 grams of Branched Chain Amino Acids (BCAAs) whereas the same amount of whey protein may provide about 11 grams of EAAs including 5-5.5 grams of BCAAs. - Amount of Calcium
Milk contains calcium so milk proteins too have calcium in them. However, Casein has more calcium than whey. Typically, about 24 grams of Casein will contain about 500 mg of calcium whereas the same amount of whey protein will provide about 140 mg of calcium.
Calcium Trivia: RDA for Calcium for healthy Indian adults is 1000 mg, typically 1 scoop of casein may provide half of your daily dietary calcium needs. - Different Types/Forms of Casein & Whey.
There are 2 types of casein protein that are commercially available.- Micellar Casein: this is the form of casein present in the milk. When casein is made in the cow, the molecules fold up into a spherical micelle. Contains many important milk minerals like calcium and phosphorus.
- Calcium Caseinate: is the denatured form of casein where casein micelle is unfolded.
- There are 3 commercially available forms of Whey Protein.
- Whey Protein Concentrate (WPC): Ranges in protein content of 34 – 80%. Higher in lactose and fat than WPI and WPH.
- Whey Protein Isolate (WPI): Up to 90% protein by dry weight. Higher % protein per gram because some lactose and fat have been reduced.
- Whey Protein Hydrolysate (WPH): Can be made from whey protein isolates or concentrate. Whey protein is “cut” into smaller units for rapid absorption.
- Best time to use/consume.
- Casein: Often used during extended timeframes (e.g., such as before bed, or between meals). Casein Protein can help support muscle recovery overnight while you sleep. Typically, casein can help support satiety, because casein forms a gel in the stomach, which may help you feel full.
- Whey: Whey being the fast digesting of the two dairy proteins, makes it a great option for consumption in the morning when your body is in catabolic state. Also, before/after workout or in between meals.
Take Home Message
Despite their differences both whey and casein are high quality complete proteins which may support muscle recovery. However, depending on your goal, you may want to go for a fast digesting whey protein closer to the workout or during the day and/or take slow digesting casein during extended fasting window or before going to the bed.

