BCAAs, or branched-chain amino acids, are essential for the body as they are obtained from proteins in foods such as meat, dairy, and legumes. Leucine, isoleucine, and valine are the specific amino acids that make up BCAAs. These amino acids have a unique molecular structure that is described as "branched-chain." BCAAs are commonly used to reduce muscle breakdown, prevent fatigue, and improve athletic performance. In this article, we will explore BCAA in depth and discuss its numerous benefits.
Table of Contents:
What are BCAAs?
Performance Benefits of BCAAs
Dietary Sources of BCAAs
Take Home Message.
What are BCAAs?
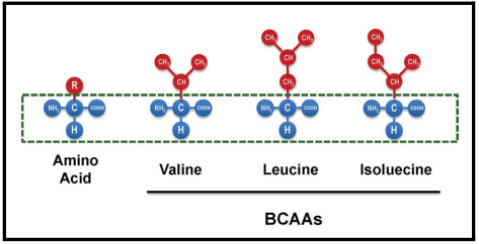
Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins, which are essential for the human body. There are 22 different amino acids, including 13 non-essential amino acids that are produced by the body and 9 essential amino acids that are obtained from diet. The shape and function of each protein are based on the specific arrangement and quantity of its amino acids. In particular, leucine, valine, and isoleucine, also known as BCAAs, are necessary for muscle energy production.
The fitness and bodybuilding community has come to love BCAAs because of their potential advantages for improving muscle growth, training efficiency, and recuperation. Furthermore, studies indicate that BCAAs may enhance immunological function and lessen tiredness during extended exercise.
BCAA is efficiently used as an energy source for working muscles. When considering athletic performance, BCAA is exceptionally beneficial for:
Performance Benefits of BCAAs
- BCAAS HELP SUPPORT MUSCLE RECOVERY: BCAAs are key building blocks to help support muscle recovery after exercise and may help spare the muscle during prolonged exercise.
- BCAAS HELP SUPPORT MUSCLE PROTEIN SYNTHESIS: Physical activity can activate mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) pathways, which signals that the muscles need to recover and rebuild. Leucine, in particular, helps to ‘switch on’ muscle protein synthesis by signaling and regulating mTOR pathways. Over time, resistance training combined with proper rest and nutrition can lead to muscle growth – otherwise known as hypertrophy.
- BCAAS CAN SERVE AS A FUEL SOURCE FOR WORKING MUSCLES: BCAAs have the potential to act as a fuel source for exercising muscle and other tissues. BCAAs can be used as fuel during prolonged activities and endurance activities like cycling and running.
Dietary Sources of BCAAs
- Chicken Breast: Leucine, one of the essential BCAAs that is vital to the synthesis of muscle protein, is found in particularly high concentrations in chicken breast, making it a lean source of protein.
- Eggs: All nine essential amino acids, which the body is unable to create on its own, are found in eggs, making them a complete protein source. The three BCAAs—leucine, isoleucine, and valine—are included in this.
- Greek Yogurt: Greek yogurt is a high-protein dairy product that has a good ratio of each of the three BCAAs. It also contains a lot of casein protein, which releases amino acids gradually due to its slow digestion.
- Quinoa: Packed with all the necessary amino acids, including BCAAs, quinoa is a special plant-based source of complete protein. It's a fantastic choice for people who eat a vegetarian or vegan diet.
- Milk: Milk is another excellent source of complete protein, containing all nine essential amino acids, including BCAAs. Milk proteins such as whey and casein are naturally high in BCAAs
1 scoop of Optimum Nutrition Gold Standard 100% Whey contains 5.5 grams of naturally occurring BCAAs.
The daily required dosage of BCAA is 5 grams per day for an average adult in a ratio of 2:1:1 (Leucine : Isoleucine : Valine) . However, athletes and individuals engaging in intense physical activity may require higher doses to support muscle recovery and growth.
Take Home Message.
BCAA can be found in high-protein foods such as meat, dairy products, and legumes. However, it may be difficult to consume enough BCAA through food alone, especially for those with specific dietary restrictions or preferences. In such cases, opting for a BCAA supplement can help ensure an adequate intake and support overall wellness. Choose from a trusted brand and follow the recommended dosage instructions for optimal results. It is also important to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to determine the appropriate dosage for individual needs.

